Elevation of the Rib Cage During Inhalation Occurs When
View the full answer. Diaphragm and intercostal muscles ascend and cause an increase in intrathoracic pressure.

Pin By Pediagenosis On Respiratory System In 2022 Upper Airway Animal Study Heimlich Maneuver
During inhalation the air coming into the lungs causes the rib cage to move upwards and outwards enlarging the chest cavity.
. This movement decrease the space in our chest cavity and the air rushes in. Diaphragm and intercostal muscles relax and cause an increase in intrathoracic pressure. Elevation of the rib cage during inhalation occurs when the intercostal muscles contract.
Rib dysfunctions can lead to chest wall pain musculoskeletal pain thoracic outlet syndrome and intercostal neuralgia. The most common dysfunction that is associated with restriction of normal rib cage motion is restriction of respiration. During inhalation the ribs move up and outward and the diaphragm moves in.
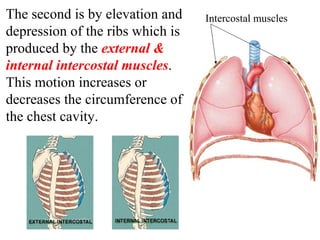
During column extension the rib cage migrates anteriorly and the ribs are elevated. Elevation of the ribs and expansion of the rib cage result from the co-ordinated action of the rib cage muscles. During inspiration the anteroposterior diameter of the.
Elevation of the rib cage during inhalation occurs when. Inhalation occurs when the. D Question 39 Which of the following occurs during inhalation.
This increases the size of the thoracic cavity and decreases the pressure inside. During exhalation the ribs moves down and inward and the diaphragm moves up. The primary motion of ribs occurs during inspiration and expiration.
Diaphragm and intercostal muscles contract and cause a decrease in intrathoracic pressure. Breathing in When you breathe in or inhale your diaphragm contracts and moves downward. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high.
When the lungs inhale the diaphragm contracts and pulls downward. At the same time the muscles between the ribs contract and pull upward. Although each rib has its own ROM occurring primarily at the costovertebral joint rib cage shifts occur with movement of the vertebral column.
A segment of the chest wall is detached from the thoracic cage. Multiple ribs are fractured on both sides of the thoracic cage. During inhalation the air coming into the lungs causes the rib cage to move upwards and outwards enlarging the chest cavity.
Hemoptysis is defined as. This movement increases the space in our chest cavity and the air is pushed out. In humans the parasternal intercostals.
This increases the space in your chest cavity and your lungs expand into it. The principal inspiratory muscle of hum. Elevation of the rib cage during inhalation occurs when the intercostal muscles contract.
During inspiration the ribs are elevated and during expiration the ribs are depressed. Decreased rib motion can lead to excess lymphatic fluid in the. A flail chest occurs when.
Rib dysfunctions occur in many forms. More than three ribs are fractured on the same side of the chest. The intercostal muscles contract.
Irritation or damage to the pleural surfaces that causes sharp chest pain during inhalation is called. The first phase is called inspiration or inhaling. They contract to pull your rib cage both upward and outward when you inhale.
Signs and symptoms of a tension pneumothorax include all of the following EXCEPT. Elevation of the rib cage during inhalation occurs when. We wished to review the action and interaction of the rib cage muscles during ventilation.
The muscles between your ribs also help enlarge the chest cavity. The rib cage is pulled up and out. Irritation or damage to the pleural surfaces that causes sharp chest pain during inhalation is called.
A segment of fractured ribs bulges during the inhalation phase. 100 1 rating Inhalation or inspiration occurs due to difference in the pressure within the lungs and external environment. Irritation or damage to the pleural surfaces that causes sharp chest pain during inhalation is called.
This article aims to identify diagnose and discuss the treatment of inhaled rib dysfunctions with direct and indirect osteopathic treatments. The parasternal intercostal muscles appear to play a predominant role during quiet breathing both in humans and in anaesthetized dogs.
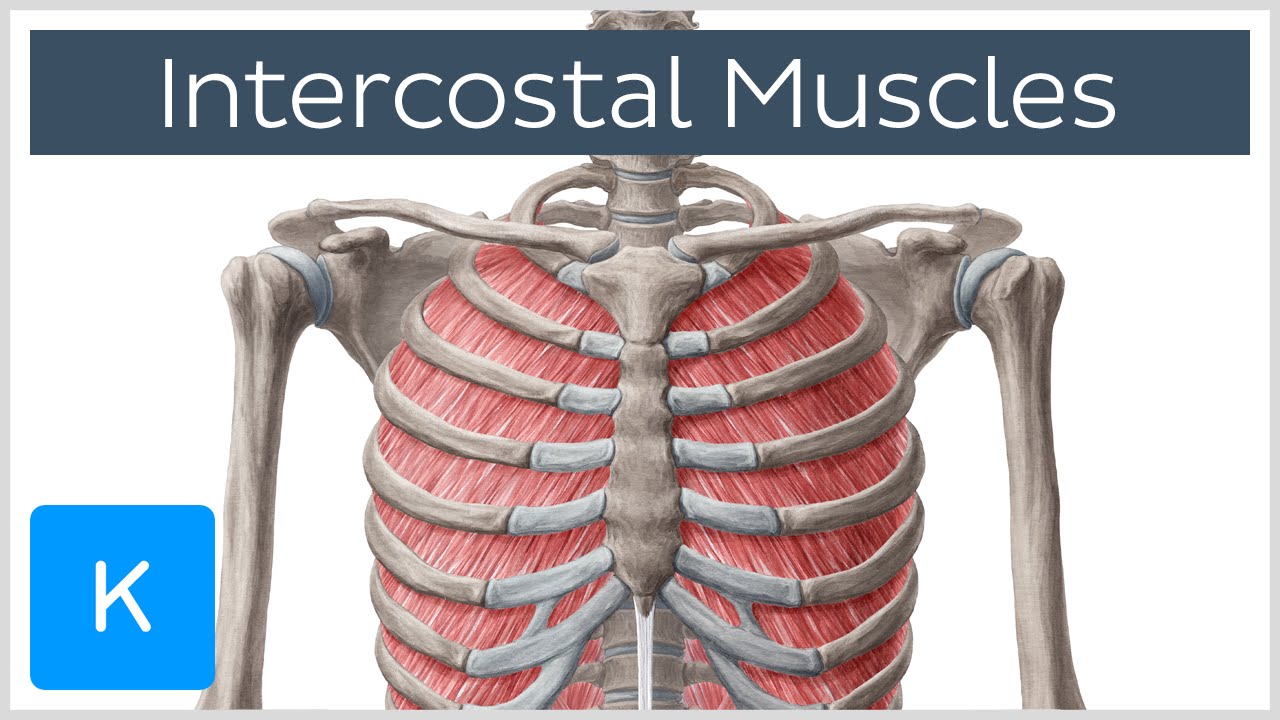
Chest Wall Anatomy Concise Medical Knowledge

Thoracic Diaphragm What Is It And Why Is It Important Rehab1 Blog Rehab1 Blog
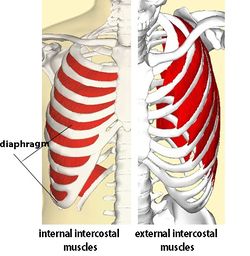
Intercostal Muscles Function Area Course Human Anatomy Kenhub Youtube
Muscles Of Respiration Physiopedia
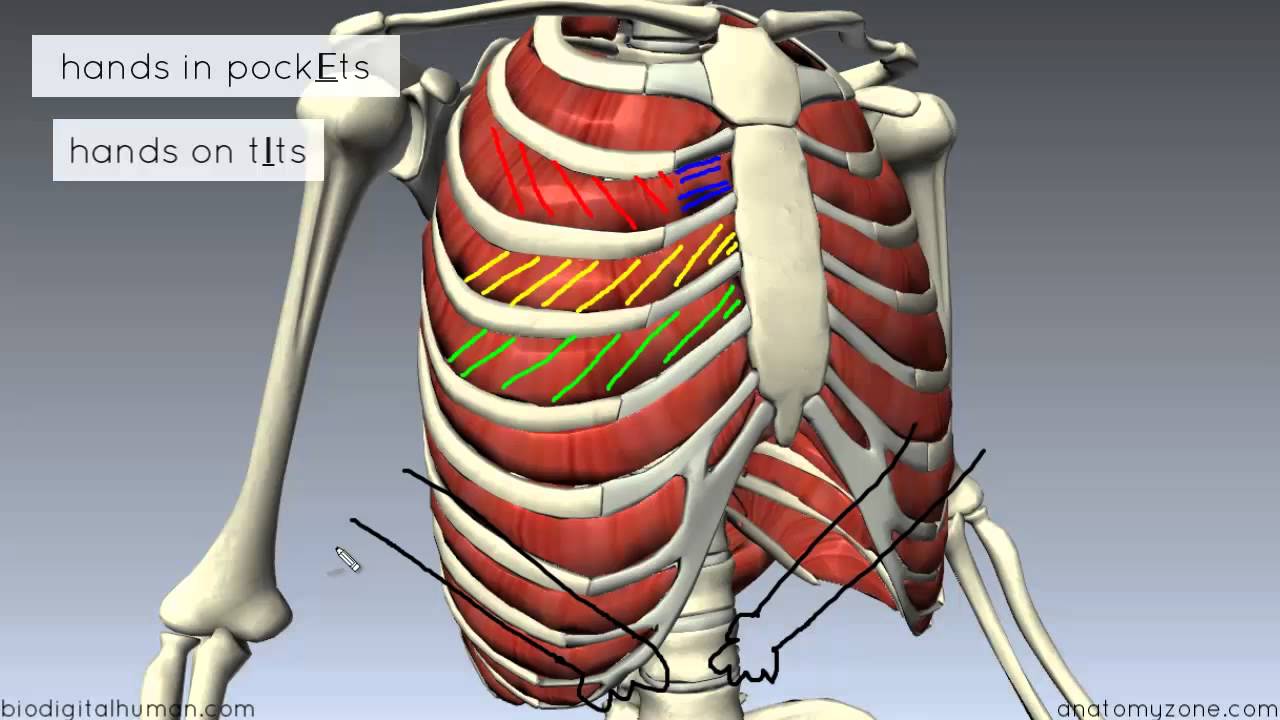
Muscles Of Respiration Physiopedia
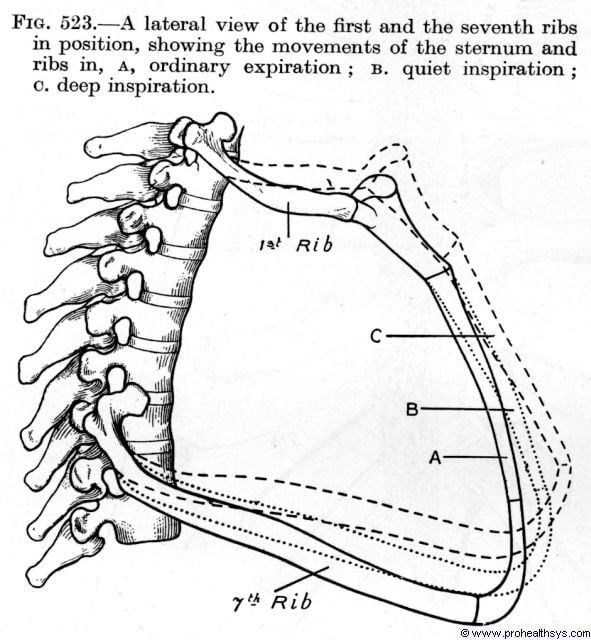
Mechanism Of Respiration Prohealthsys
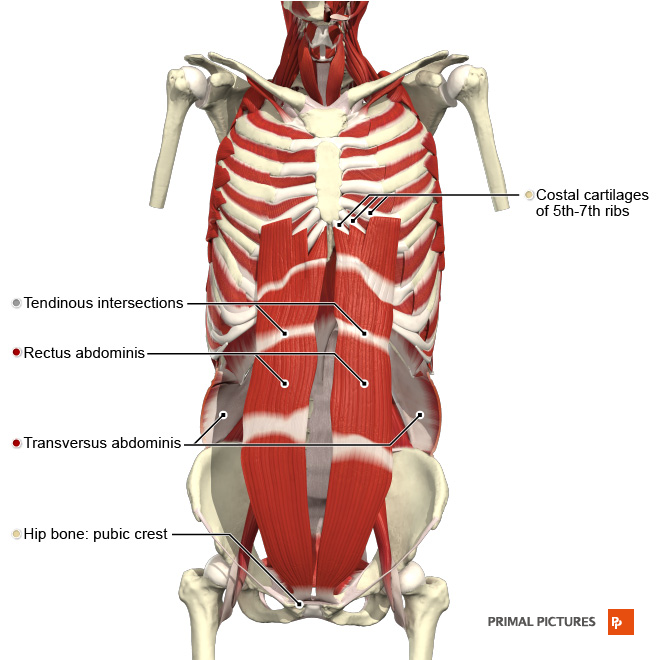
Muscles Of Respiration Physiopedia

Human Respiratory System Muscle And Lung Receptors Britannica

Intercostal Muscle Strain Physiopedia

St Segment Gross Elevation Is Often Described As Tombstoning Or A Fireman S Hat St Elevation Nursing Notes St Depression
Elevated First Rib Is An Underappreciated Cause Of Neck And Shoulder Pain Pt360

Shortness Of Breath Lung Health A Z Chest Foundation

Human Respiratory System The Mechanics Of Breathing Britannica
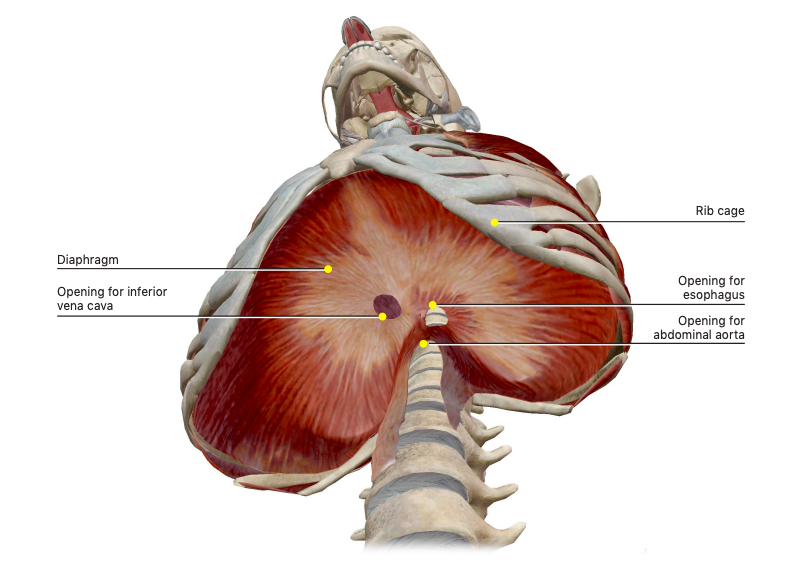
Solved Rib Cage Diaphragm Opening For Inferior Vena Cava Chegg Com

Comments
Post a Comment